Did you know that over 350-450 languages are being spoken in U.S. households? As of 2023, it’s estimated that over 67.8 million people (nearly double the population of California) speak a language other than English, making our nation one of the most linguistically diverse countries in the world. But while our growing diversity is something to be proud of, it’s important to recognize that linguistic diversity presents opportunities and challenges.
For our healthcare system, it’s important to know that hospitals are dealing with an increasing number of patients who don’t speak English as their primary language. This trend highlights a growing need for healthcare interpretation since failure to bridge the language gap can deter treatment and equitable care.
Over the years, medical interpreters have served as conduits between healthcare providers and patients with limited English proficiency (LEP). By facilitating medical appointments, emergencies, and other important discussions, their efforts have allowed ethnic minorities, refugees, and people who belong to rare language communities to navigate through the intricacies of our country’s healthcare system. In this guide, we’ll provide a brief breakdown of medical interpreters, discuss how medical interpretation works, and more.
What is a Medical Interpreter?
A medical interpreter is a language professional who facilitates communication in the healthcare setting. Medical interpreters support patients (and their accompanying persons) by allowing them to communicate naturally with doctors, nurses, hospital staff, and administrators.
Each interpretation setting has unique challenges; the medical field is no exception. Unlike community interpreters who work across different domains, medical interpreters focus specifically on healthcare contexts. Since healthcare discussions are filled with complex terminologies and jargon, facilitating engagements without formal training can increase the risk of miscommunication and compromise a patient’s well-being. Medical interpreters undergo specialized and rigorous training to ensure accurate and nuanced communication between patients and healthcare providers.
How Does Medical Interpretation Work
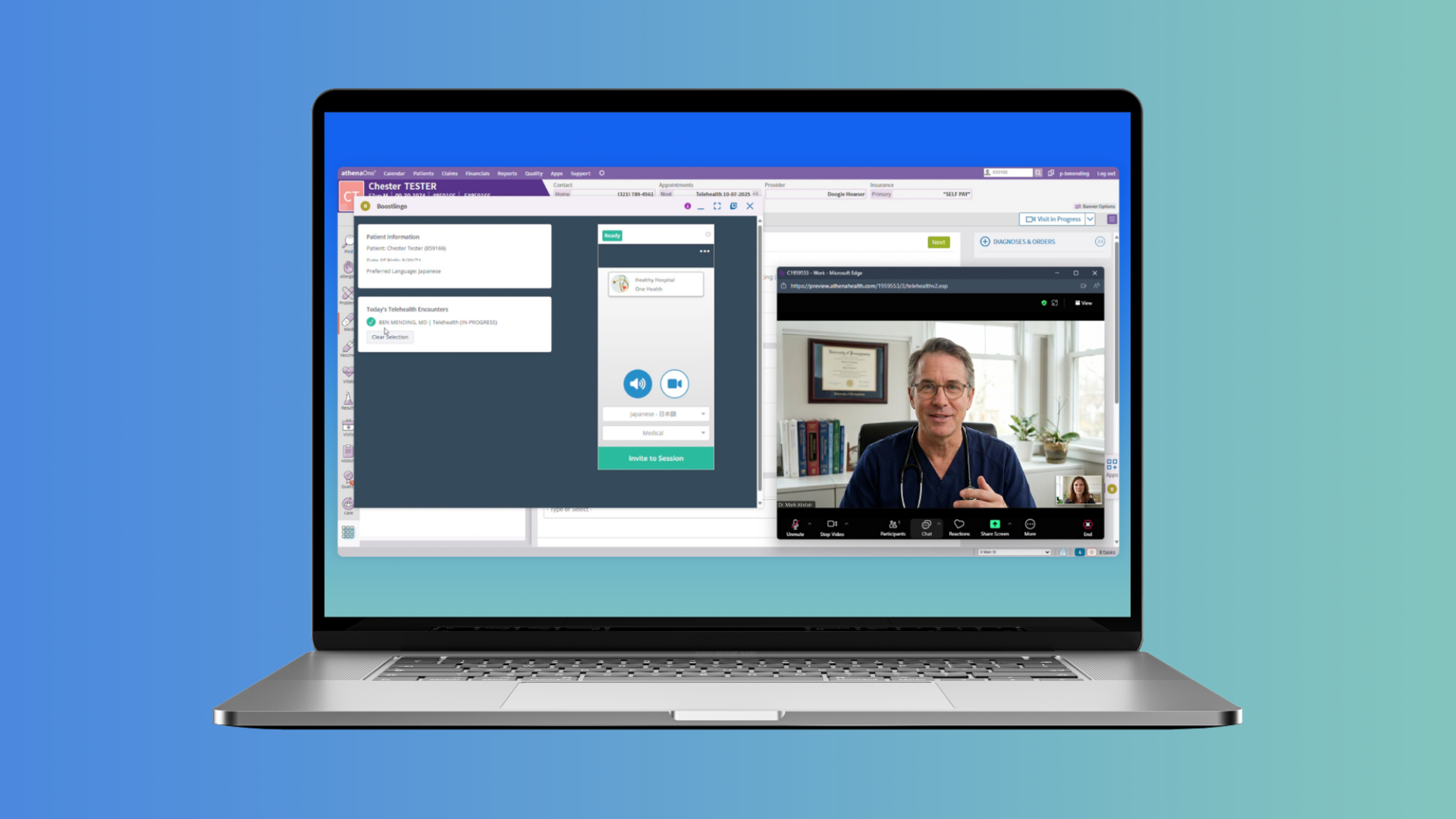
With the entrance of Video Remote Interpreting (VRI) and Over the Phone Interpreting (OPI), interpreting services can now be conducted virtually. In 2023, 49% of interpreting was delivered remotely, and the COVID-19 pandemic further propelled the shift to remote interpretation. Today, healthcare providers continue to rely on remote interpreting for medical interpretation due to its benefits, such as cost-friendliness, convenience, and availability. But whether language support is provided on-site or traditionally, medical interpretation generally follows this procedure:
- A healthcare professional needing language support will request the assistance of a medical interpreter. Depending on the healthcare center’s capacity and language access plan, an interpreter may arrive on-site or be accessed remotely.
- The interpreter establishes a connection with the patient and the healthcare provider. By actively listening to the participants, the interpreter analyzes information, takes note of linguistic nuances and complex terminologies, and then reformulates messages between both parties.
- The process repeats until the medical encounter is finished. Thanks to the medical interpreter’s expertise, the patient and healthcare provider can express themselves naturally and fully, improving the patient’s experience.
Challenges in Medical Interpretation
Effective communication is essential in healthcare settings because language barriers can significantly impact treatment. Contrary to best practices, some healthcare organizations rely on bilingual staff or the bilingual companions of a patient for interpretation. If a bilingual person has not received training as an interpreter, it’s likely that information will be wrongfully exchanged. While relying on bilingual staff and companions can sometimes be okay for casual discussions, there are significant risks to the practice for medical appointments and emergencies.
When healthcare providers and patients exchange medical information (e.g., medical history, treatment options, etc.), discussions are filled with difficult terminologies that can be hard to relay in another language without formal training. Moreover, some words and phrases don’t have a direct English equivalent or can mean something else depending on context or the patient’s culture. Overall, there are unique complexities in healthcare that only qualified medical interpreters can navigate.
Cultural and linguistic nuances
Cultural sensitivity and linguistic nuances add another layer of complexities to medical interpretation. Interpreters must be knowledgeable of patients’ cultural backgrounds, beliefs, and communication styles since these factors can greatly affect their perception of their health, treatment options, and more. Extensive knowledge of the medical field and cultural sensitivity are equally important in medical interpretation since both factors help healthcare providers bridge and build rapport with their patients.
Navigating through high-stress and emotional situations
Hospitals and healthcare centers are high-pressure environments, and medical interpreters participate in the struggles of doctors and nurses. Since they work side-by-side with them, they often witness patients’ pain, suffering, and despair. Having to deliver distressing news, seeing an injured person get rushed to the emergency room, and other high-pressure situations can be emotionally taxing.
Interpreters must practice strong emotional resilience to challenging situations since failure to do so may affect the quality of their interpretations. Maintaining composure and establishing boundaries are necessary to ensure accurate and unbiased communication between parties. Being able to navigate through emotional situations effectively ensures that patients receive the support and understanding they need as they go through the vulnerable moments on their road to recovery.
HIPAA Compliance and Security
Protecting sensitive patient information is mandated by law, so medical interpreters must follow ethical guidelines and comply with federal regulations. Laws such as The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) set strict guidelines for hospitals and all other organizations that cater to the health sector on how they should handle, store, and transmit protected health information (PHI).
Healthcare centers are continuously transitioning toward the digital space, and while this digital transformation has optimized workflows, reliance on modern technologies emphasizes the growing threat of cybercrime. According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report, the global average cost of a data breach in 2023 was USD 4.45 million, and this marks a 15% increase over the past three years. To prevent the leakage of medical records, billing information, and communication, medical facilities must continuously improve their security infrastructure and conduct compliance training for staff.
HIPAA compliance poses a unique challenge for interpreters since they often find themselves in situations where they are tasked to handle and process a patient’s sensitive data. They must practice discretion and confidentiality when providing language support, so they must undergo training to adhere to HIPAA requirements and maintain regulatory compliance as they facilitate discussions. Additionally, understanding the dangers of leaking PHI and having a secure communication infrastructure ensures that violations and data breaches are prevented.
Medical Interpretation and Medical Translation Services: What’s the Difference?
Interpretation and translation are two distinct terms that are often used interchangeably. In the medical field, interpreters facilitate communication between patients and healthcare providers who speak different languages. In contrast, medical translators ensure that the contents of important documents (e.g., medical information forms and consent waivers) can be read and understood by patients in their preferred language.
Both occupations have the same end goal of overcoming the language barrier in healthcare. However, they are separate professions with distinct training and certifications. Translators may be qualified to analyze and reformulate documents but may not necessarily be qualified to interpret a real-time discussion between a doctor and a patient. On the other hand, interpreters may be fit to facilitate a medical appointment or emergency but may only be qualified to translate sensitive documents with the necessary certifications.
If you want to learn more about the differences between both professions, read our comprehensive guide to interpretation services.
Bridging the Language Gap Through On-Demand Medical Interpretation
Over the years, it’s expected that the linguistic diversity of the United States will continue to grow. Medical centers will need to adapt to the ever-evolving healthcare landscape since the language access needs of their hospital may fluctuate through the years. To successfully bridge the language gap in healthcare, hospitals must constantly monitor their local community’s population, stay on top of refugee crises and immigration patterns, and implement an on-demand language access plan that will grant easy access to quality healthcare interpretation.
If you’re seeking a health equity partner who can provide language support on-demand, look no further than Boostlingo. The qualified interpreters in our professional network have specialized training and experience in the medical field, and partnering with us will allow you to build the ideal patient experience and achieve health equity. We have comprehensive plans that can suit the needs of different healthcare centers, and you’ll be glad to know that we offer language support for in-demand medical languages such as: